Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition
Large number of competing firms
Vendors in a big food court at the mall
Gas stations along a major highway
Differentiated Products
Similar but not identical products
Various types of chocolate candy: Twix, Snickers, M\&Ms…
Free entry and exit in the long run
If there are opportunities for profit, firms can enter
Similarly, if there is loss companies will exist
Unlike perfect competition, there's pricing power
Unlike monopoly, there's competition
Unlike oligopoly, there are many firms
Graph
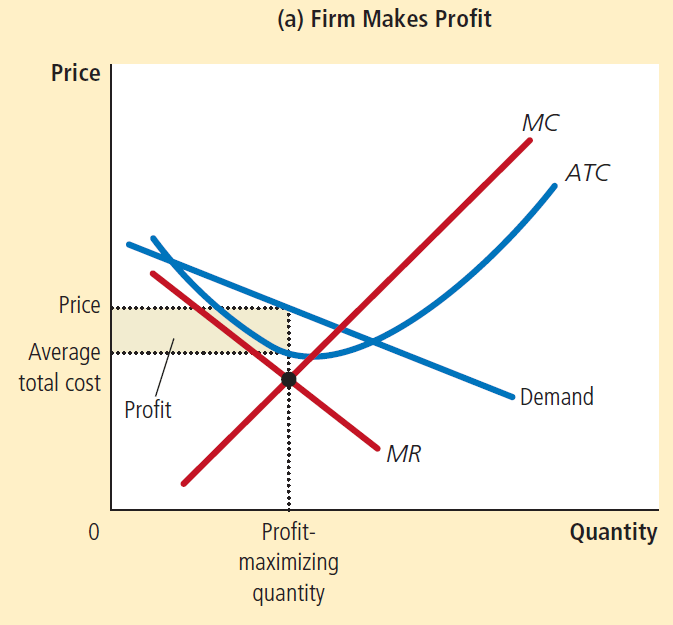
Profitable firm in monopolistic competition
Graph similar to a monopoly earning economic profit
Demand curve is slightly more elastic in monopolistic competition than in monopoly
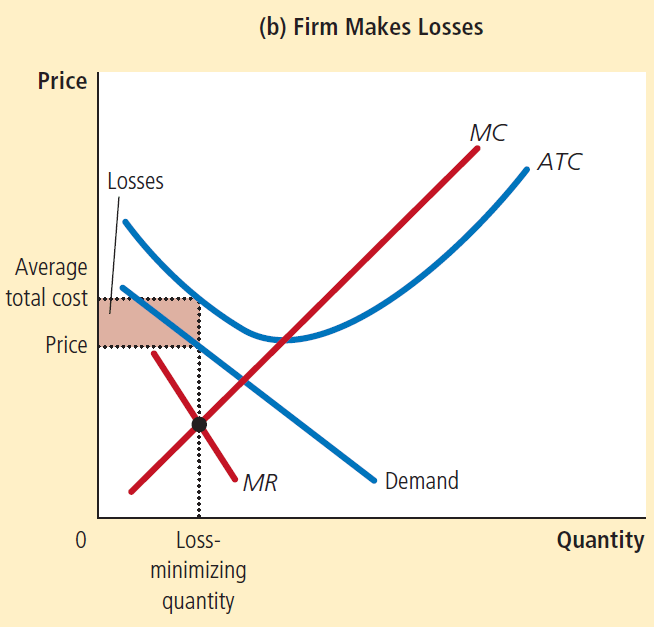
Unprofitable firm in monopolistic competition
Graph similar to a monopoly incurring economic loss
Demand curve is slightly more elastic in monopolistic competition than in monopoly
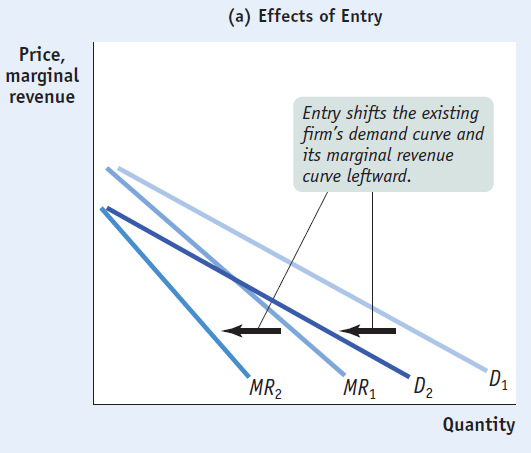
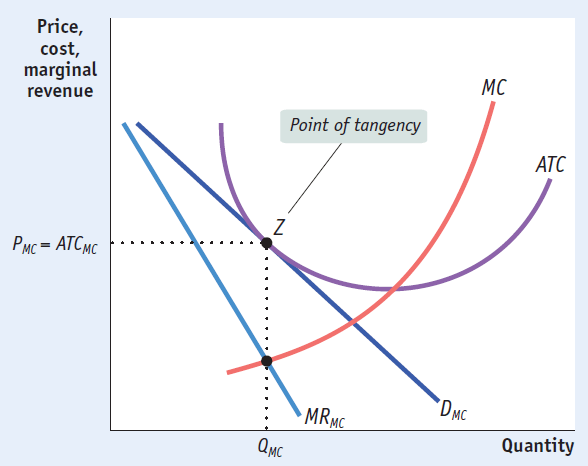
Long-Run Zero-Profit Equilibrium
If profitable, firm entry will occur and individual firm demand will shift left
If unprofitable, firm exit will occur and individual firm demand will shift right
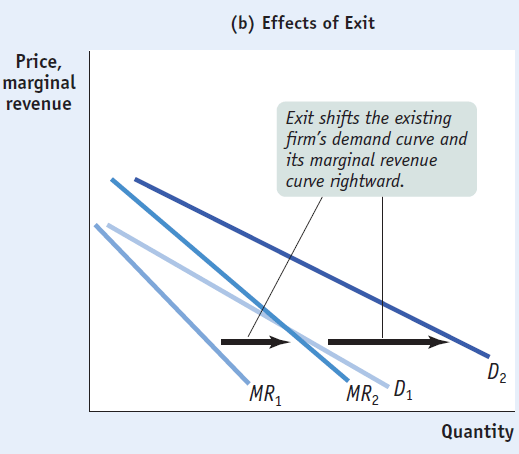
In long-run, demand curve will be tangent to its ATC at its profit-maximizing point
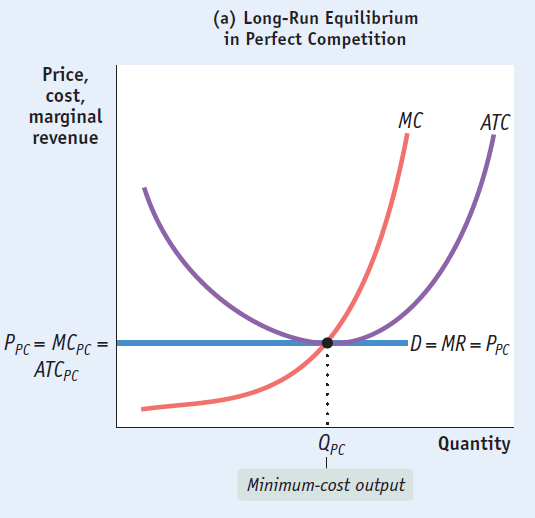
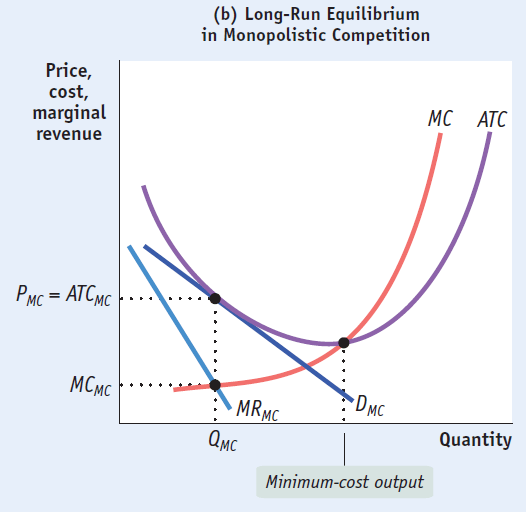
Comparing Perfect & Monopolistic Competition
Both make zero economic profit
Perfect competition operates at both minimum ATC and where P = MC.
Both productively and allocatively efficient
Monopolistic competition operates to the left of minimum-cost output and has excess capacity
Product Differentiation & Advertising
How firms differentiate their products
Differentiation by style or type
Differentiation by location
Differentiation by quality
Ford vs. General Motors
Henry Ford famously quipped that customers could the Model T in "any color, so long as it's black"
Alfred Sloan challenged this perfectly competitive view of automobiles
Even though more expensive, consumers preferred the range of styles and GM became the dominant car brand during the 20th century
Monopolistic Competition Example
Assume a city eliminates the license fee (fixed cost) for all firms in a monopolistically competitive industry.
How is output affected?
Not affected
Because marginal cost stays the same.
How is economic profit affected?
FC↓, TC↓, ATC↓
can make economic profit
Firms enter, demand increases, and drives out profit